Security Guard vs. Bodyguard vs. Security Officer: Key Role Differences Explained
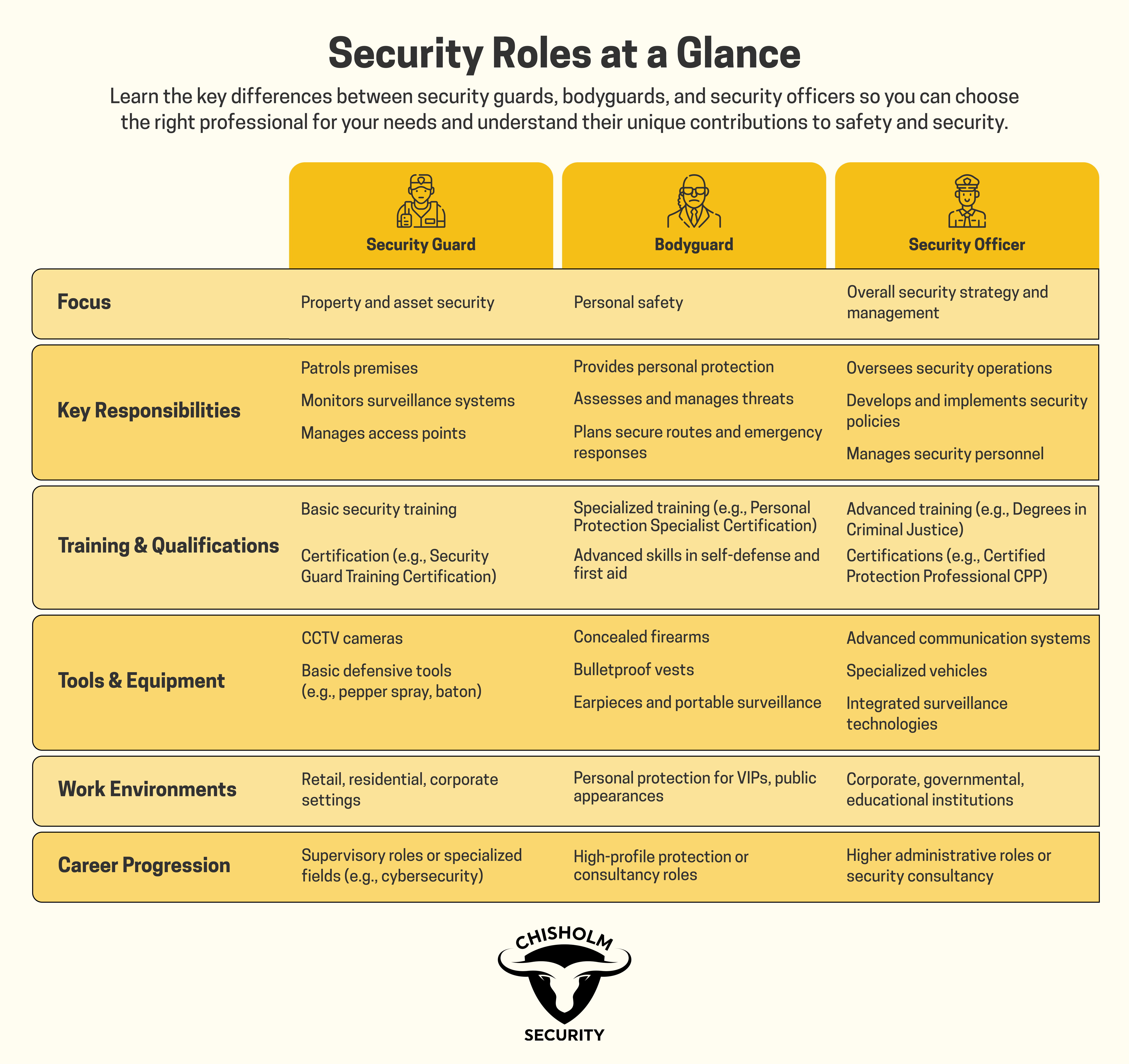
Choosing between a security guard, a bodyguard, and a security officer can seem challenging, but understanding their distinct roles makes the decision clearer. A security guard typically monitors and patrols premises to prevent theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access. In contrast, a bodyguard provides personal protection to individuals, often dealing with direct threats and ensuring the safety of their clients in various environments.
Security officers generally hold more advanced positions and may oversee teams of security guards, manage security operations, and maintain detailed reports. While they share some similarities, each role requires different training, qualifications, and skill sets. Knowing these distinctions helps you select the right type of security professional for your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Security guards monitor and patrol premises to prevent incidents.
- Bodyguards offer personal protection and handle direct threats.
- Security officers manage security operations and teams.
Defining the Roles
Security guards, bodyguards, and security officers each have distinct roles and responsibilities that contribute to a comprehensive security strategy. Understanding these roles helps us appreciate their unique contributions and how they integrate with video security systems to enhance overall security operations.
Security Guard Basics
Security guards are primarily responsible for safeguarding property and assets. Their duties often include monitoring surveillance equipment, patrolling designated areas, and checking for potential security breaches.
Interaction with Video Security Systems:
- Monitoring and Response: Security guards typically end up stationed at locations such as building entrances, parking lots, and public events. They frequently monitor live video feeds to detect and respond to suspicious activity. For example, at a large shopping mall, security guards use video surveillance systems to oversee foot traffic and identify any unusual behavior or potential threats.
Real-World Example: In 2020, during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, a major retail chain in the U.S. deployed security guards to enforce health and safety protocols. Guards were equipped with real-time video surveillance feeds that allowed them to monitor customer compliance with mask-wearing and social distancing measures. This integration of video systems helped reduce conflicts and ensure adherence to safety guidelines, contributing to a safer shopping environment.
Training and Skills: Security guards receive training in basic security procedures, emergency response, and customer service skills. Their ability to effectively use video surveillance systems enhances their capacity to maintain a secure environment, respond to alarms, and report suspicious activity.
Bodyguard Fundamentals
Bodyguards are responsible for the personal protection of high-profile individuals such as celebrities, politicians, or executives. Their focus is on ensuring the safety of their clients, which involves conducting risk assessments and planning secure routes.
Interaction with Video Security Systems:
- Coordination and Awareness: While bodyguards are primarily focused on personal protection, they often rely on video security systems for situational awareness. They coordinate with security officers to access video feeds that provide insights into potential threats and assess the safety of environments before their clients arrive.
Real-World Example: During the 2022 World Economic Forum in Davos, bodyguards for several high-profile attendees worked closely with security teams managing extensive video surveillance systems. The video feeds allowed bodyguards to monitor crowd movements and identify any potential threats in real time. This coordination ensured that the protected individuals could navigate the event safely and avoid potential risks.
Training and Skills: Bodyguards are trained in defensive tactics, first aid, and sometimes advanced driving techniques. They use video surveillance data to enhance their protective measures, allowing them to anticipate and respond to threats effectively.
Security Officer Overview
Security officers typically hold supervisory or managerial roles, with responsibilities for overseeing security operations, developing policies, and managing security personnel. Their role often involves integrating video security systems into broader security strategies.
Interaction with Video Security Systems:
- Management and Integration: Security officers oversee the implementation and maintenance of video surveillance systems, ensuring they are integrated with other security measures. They analyze video data to identify trends and potential vulnerabilities, refine security protocols, and conduct regular security audits.
Real-World Example: At a major international airport, security officers are responsible for managing an extensive network of video surveillance cameras. In 2018, a sophisticated integration project was undertaken to upgrade the airport’s security infrastructure. The security officers played a crucial role in overseeing the installation of new high-definition cameras and integrating them with the existing access control systems. This enhanced capability allowed for more effective monitoring of critical areas, such as baggage claim and security checkpoints, leading to improved incident response times and overall security management.
Training and Skills: Security officers receive advanced training in risk management, emergency planning, and the use of advanced security technologies. Their expertise ensures that video surveillance systems are effectively integrated into security operations, contributing to enhanced organizational safety and responsiveness.
Training and Qualifications
Each role has specific requirements that set them apart, especially in the context of advanced security systems and cybersecurity.
Education and Certification
All security roles require training and certification:
- Security Guards: Typically need to complete basic training programs focused on general security procedures. A common certification involves the Security Guard Training Certification, which covers foundational security practices and the use of surveillance equipment.
- Bodyguards: Require specialized certifications such as Personal Protection Specialist Certifications. Their training often includes threat assessment, crisis management, and specific skills related to high-risk environments.
- Security Officers: Generally possess a combination of education and certification. Degrees in criminal justice are common, alongside certifications like the Certified Protection Professional (CPP) from ASIS International. This certification covers advanced aspects of security management, including the integration of security systems and strategic planning.
Technical Skills and Cybersecurity
The growing complexity of security threats emphasizes the importance of technical skills in handling advanced security systems, data protection, and cybersecurity.
- Cybersecurity and Data Protection: Security officers, in particular, benefit from specialized training in cybersecurity. The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification is highly relevant for those focusing on cyber threats. This certification covers a broad range of security topics, including risk management, network security, and data protection strategies.
- Advanced Security Systems: Understanding and managing sophisticated video surveillance systems is crucial. Security officers often oversee the integration of these systems into broader security operations, requiring expertise in the latest technologies and industry standards.
Specialized Skills Training
Each role may require unique, specialized skills. For instance, security guards often receive crowd control and emergency response training. Bodyguards need advanced skills like evasive driving and specialized first aid to protect high-profile clients.
Security officers might acquire skills in cybersecurity, surveillance technology, and conflict de-escalation. Advanced training programs often align with their professional growth and the specific needs of their employers. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is a sought-after certification for security officers focusing on cyber threats.
In this way, tailored training and qualifications equip us with the skills to perform our specific roles efficiently. Structured and specialized training programs help security personnel better prepare to face diverse challenges.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Adhering to industry standards and obtaining relevant certifications are key to professional growth and effective performance. ASIS International sets standards for security practices, and certifications like CPP and CISSP help ensure that security professionals are well-equipped to handle the evolving landscape of security threats and technologies.
Typical Responsibilities
In this section, we will delve into the typical responsibilities of security guards, bodyguards, and security officers, categorizing them into surveillance, patrols, and emergency response.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Security guards, bodyguards, and security officers all rely on advanced video surveillance technologies to enhance their ability to prevent unauthorized activities and ensure safety.
- Security Guards: In addition to their traditional duties of patrolling and visual inspections, security guards now leverage video surveillance systems for remote monitoring, allowing them to oversee multiple areas simultaneously from a central location. For example, at large facilities like shopping malls or office complexes, guards use live video feeds to monitor entrances, parking lots, and interior spaces, enabling them to respond quickly to any incidents. AI-driven threat detection systems can further assist by automatically identifying unusual behavior or potential threats and alerting guards in real time.
- Bodyguards: Bodyguards use video surveillance to enhance personal protection for individuals in public spaces. By integrating video feeds with mobile devices or personal security systems, bodyguards can receive real-time updates about their client’s surroundings. AI-driven analytics help in preemptively identifying potential threats, such as unusual crowd movements or unauthorized persons near the client, allowing bodyguards to take proactive measures to ensure safety during public appearances or travel.
- Security Officers: Security officers manage and analyze video feeds to detect and respond to security breaches promptly. Advanced video analytics and AI-driven threat detection systems are employed to monitor large-scale operations, such as corporate campuses or critical infrastructure. These technologies help officers identify risks, detect anomalies, and generate actionable insights, facilitating quicker decision-making and more effective security management.
Examples of Effective Integration
- Remote Monitoring in a Corporate Environment: At a major financial institution, security officers integrated video surveillance systems with AI-driven analytics to monitor multiple branches. The system’s ability to analyze video feeds and detect unusual patterns, such as unauthorized access or suspicious behavior, allowed officers to respond proactively and mitigate potential security risks before they escalated.
- AI-Driven Threat Detection for Public Events: During a high-profile public event, bodyguards used video surveillance combined with AI-powered threat detection to ensure the safety of VIP attendees. The system identified and alerted security personnel to potential threats based on real-time analysis of crowd movements and behavior, enabling timely interventions and enhancing overall event security.
By incorporating advanced video security systems into their routine responsibilities, security professionals can significantly enhance their effectiveness. Remote monitoring and AI-driven threat detection not only improve their ability to respond to immediate threats but also contribute to a more proactive and comprehensive approach to security management.
Patrols and Access Control
Regular patrols help deter criminal activities and ensure the safety of the premises. During patrols, they check for open windows or doors, unauthorized personnel, and other security breaches.
Access control involves verifying the identity of individuals entering secured areas. Security officers often manage access controls by checking identification and logging entries and exits.
Bodyguards, on the other hand, may perform access control to secure their client’s space from unauthorized persons by coordinating with other security personnel and using sophisticated systems.
Emergency Response and Incident Management
Integrating real-time video feeds into these processes can significantly enhance how incidents get managed and how security teams coordinate with law enforcement.
Real-Time Video Feeds in Incident Management
- Security Guards: Security guards are often the first to respond to emergencies such as fires, medical incidents, or security breaches. Real-time video feeds play a crucial role in their response efforts by providing immediate visual information about the incident. For example, if an alarm is triggered due to a fire, security guards can use live video feeds to assess the situation from a safe distance, identify the location of the fire, and determine the best evacuation routes. Real-time information allows them to execute evacuation procedures more effectively and guide emergency responders to the exact location.
- Security Officers: Security officers are responsible for conducting risk assessments and developing incident protocols. Security officers utilize real-time video feeds for their role in coordinating with external emergency services and managing incidents. During an incident, security officers can use video feeds to monitor the situation, assess the effectiveness of their response strategies, and provide detailed information to law enforcement. For example, during a lockdown situation at a corporate facility, security officers can share live video feeds with police to help them understand the layout of the facility, the location of intruders, and any potential hazards, thus improving response efficiency.
- Bodyguards: Bodyguards need to implement immediate, personalized response plans for their clients, which often involve real-time threat assessment and coordination. Video surveillance systems allow bodyguards to continuously monitor their client’s environment, providing crucial information that helps in developing escape routes and ensuring safe transport. For instance, during a high-profile public appearance, bodyguards can use live video feeds to track crowd movements, detect potential threats, and adjust their protective measures in real time.
Examples of Effective Use
- Corporate Facility Lockdown: In an incident at a large corporate campus, security officers used real-time video feeds to manage a lockdown situation. The live footage allowed them to monitor the whereabouts of the suspect and direct law enforcement accurately. The ability to provide real-time updates and detailed visual information significantly expedited the police response and resolution of the incident.
- Public Event Security: During a major public event, bodyguards utilize real-time video feeds to enhance the security of a VIP guest. By continuously monitoring video feeds from various angles, they were able to detect and respond to potential threats swiftly. The integration of live video allowed them to adjust their security strategy dynamically and ensure the client’s safety throughout the event.
Incorporating real-time video feeds into emergency response and incident management not only improves situational awareness but also enhances coordination with law enforcement. By providing immediate visual information, security personnel can respond more effectively to emergencies, streamline incident management, and ensure the safety of people and properties.
Key Differences Between Roles
Security guards, bodyguards, and security officers each have unique responsibilities and skill sets. We need to understand their roles to appreciate their specific functions in maintaining safety and security.
Risk Assessment and Management
Security guards often focus on routine checks and monitoring environments such as malls or office buildings. They evaluate daily risks like theft or vandalism. Bodyguards, on the other hand, specialize in assessing threats to individuals, particularly high-profile clients, and tailor their strategies to these risks. Security officers, usually responsible for larger operations, manage complex risk assessments that include both physical and cyber threats.
A security guard might patrol and report suspicious activities. A bodyguard conducts a more nuanced risk assessment, including planning escape routes and vetting public appearances. Security officers create comprehensive risk management plans and direct other security personnel in their implementation.
Personal Protection vs. Asset Security
Personal protection and asset security require different approaches. Bodyguards are dedicated to the personal safety of their clients. They protect individuals from physical harm, whether during travel, public appearances, or in private life. The role demands constant vigilance and immediate reaction to threats.
Security guards focus more on asset protection. They guard property, equipment, or other valuable assets by monitoring surveillance systems, conducting perimeter checks, and controlling access points. Security officers, bridging the gap, ensure both personal and asset security within larger operations, often involving the coordination of multiple security measures and teams.
Level of Authority and Use of Force
The level of authority and use of force varies significantly. Security guards typically have limited authority and follow strict guidelines for the use of force, often limited to deterring criminal activities and reporting to police if needed. They are usually unarmed or equipped with non-lethal tools.
Bodyguards frequently possess a higher level of authority in their specific context, which may include carrying firearms depending on the jurisdiction and client’s requirements. Their use of force is more proactive and focused on the immediate safety of their client.
Security officers oversee security protocols and personnel. They have the authority to make strategic decisions and deploy force if necessary, balancing physical security measures with compliance with legal and organizational policies.
Work Environments and Sectors
Security roles vary significantly across different environments and sectors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial to determining the right type of security professional for specific needs. Here, we explore the working environments of security guards, bodyguards, and security officers.
Corporate and Commercial Security
Security guards and officers protect businesses, corporate offices, and commercial areas by monitoring entrances, ensuring compliance with security protocols, and managing visitor access.
These professionals are often tasked with patrolling premises, responding to alarms, and handling emergencies. They may also be responsible for securing sensitive information and ensuring the physical safety of employees and assets. High-end commercial properties might require security personnel to coordinate with local law enforcement for enhanced protection.
Event Security and Crowd Control
Security guards in event security roles are trained to manage crowd control, prevent unauthorized access, and deal with any disruptive behavior swiftly.
Chisholm Security’s use of cutting-edge surveillance technology sets us apart in event security. We employ AI-driven analytics to monitor for suspicious activities, such as unattended bags or unusual crowd movements, enabling us to respond promptly and prevent incidents before they escalate. Our surveillance systems are designed to cover large areas efficiently, ensuring that every corner of the venue is secure.
Protection for Individuals and VIPs
Bodyguards specialize in the personal protection of individuals, including VIPs and celebrities. Unlike security officers who protect property, bodyguards focus on the safety of a specific person. They are frequently seen in high-risk situations and often work in residential areas or accompany clients to various locations.
These professionals conduct threat assessments, devise security plans, and remain constantly vigilant. Their responsibilities include not only physical protection but also ensuring the privacy and personal space of their clients. High-profile clients often require discreet yet highly effective protection, making this a specialized and demanding field.
Tools of the Trade
The effectiveness of security personnel greatly depends on the tools and equipment they use. In modern security operations, technology, including video surveillance and remote monitoring, plays a critical role.
Safety Equipment and Technology
Safety Gear: Essential equipment includes vests, helmets, and gloves, which provide protection in potentially hazardous environments. For bodyguards, bulletproof vests are common to guard against ballistic threats. Security guards might use similar gear, depending on the environment and the potential risks they face.
Technology in Safety: Advanced video surveillance systems allow personnel to monitor areas in real-time, identifying and assessing threats without direct confrontation. Remote monitoring capabilities enhance this further, enabling security teams to respond to incidents swiftly and with greater precision.
Communication and Surveillance Systems
Effective communication and surveillance aid in managing security operations efficiently.
- Bodyguards: Employ discreet earpieces and handheld radios to maintain constant communication. Portable surveillance devices, such as body-worn cameras, can record interactions and provide real-time visual information, supporting bodyguards in maintaining situational awareness and coordinating their protective measures.
- Security Guards: Use two-way radios for communication and may have access to CCTV systems to oversee large areas. The integration of video surveillance allows them to monitor multiple locations simultaneously and respond to incidents more effectively.
- Security Officers: Operate with complex communication networks, including alarm systems, intercoms, and real-time surveillance technologies, enabling them to track activities across large facilities, coordinate responses with other security teams, and liaise with law enforcement agencies as needed.
Vehicles and Defensive Driving
Mobility and defensive driving are crucial aspects of security operations, particularly in high-risk situations.
- Bodyguards: Drive armored vehicles designed to withstand attacks and employ evasive driving techniques to ensure the safety of VIPs. These vehicles are often equipped with advanced communication and surveillance systems, enhancing their ability to respond to threats while on the move.
- Security Guards: Typically use standard vehicles for patrolling, which may include secure, fenced areas for enhanced safety. Visibility and deterrence are key functions of these vehicles, which are often equipped with basic communication tools.
- Security Officers: They may have access to a fleet of specialized vehicles, some equipped with communication and surveillance systems. These vehicles support rapid and coordinated responses to incidents, providing enhanced coverage and operational efficiency.
By integrating specialized equipment and leveraging advanced technology, security personnel can effectively respond to the diverse challenges they encounter. The use of video surveillance and remote monitoring, combined with rigorous training, enhances their ability to maintain safety and manage incidents efficiently.
Skills and Competencies
Some key skills and competencies include technical proficiency with video systems, data analysis, and cybersecurity, alongside strategic planning and security management.
Technical Proficiency and Data Analysis
Video Systems Expertise: In today’s security landscape, proficiency with advanced video surveillance systems is crucial. Security personnel must be adept at operating and troubleshooting these systems to ensure continuous monitoring and effective incident response. For example, security officers are often responsible for selecting and managing video security systems that integrate with other technologies, providing comprehensive coverage and real-time data.
Data Analysis: Security personnel must analyze data from video feeds and other surveillance sources to identify patterns and potential threats. The process involves interpreting video footage, understanding alarm triggers, and using analytics tools to enhance situational awareness. Effective data analysis enables security teams to anticipate and address security issues proactively.
Cybersecurity: Security personnel need to understand how to protect video surveillance systems from cyber threats and ensure data integrity. Training in cybersecurity protocols and practices helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches, safeguarding sensitive information.
Strategic Planning and Security Management
Security Planning: Strategic planning involves developing and implementing comprehensive security protocols tailored to specific environments. Security officers, in particular, are responsible for creating and updating security plans that address potential risks and threats, including selecting the appropriate video security systems, integrating them with other security measures, and ensuring they meet the needs of the facility or event.
Security Management: Effective security management requires overseeing the implementation of security strategies and ensuring they are executed efficiently, including coordinating with various departments, managing resources, and conducting regular reviews of security protocols. Security officers play a key role in managing these aspects, ensuring that security measures are robust and adaptive to evolving threats.
Example: For instance, at a large corporate campus, security officers may be responsible for integrating video surveillance systems with access control and alarm systems. They ensure that all components work seamlessly together, providing a comprehensive security solution that allows for real-time monitoring and quick response to incidents.
By focusing on technical proficiency with video systems, data analysis, and cybersecurity, alongside strategic planning and security management, security personnel can effectively handle modern security challenges, ensuring security measures are not only reactive but also proactive, providing robust protection and enhancing overall safety.
Career Paths and Industry Insights
When exploring career options in the security field, potential roles such as security guards, bodyguards, and security officers each offer unique opportunities and challenges. Understanding the progression and required regulations helps in making informed career choices.
Career Progression and Opportunities
Security guards often start with basic duties such as patrolling premises and monitoring surveillance systems. As they gain experience, opportunities for advancement can include supervisory positions, managing teams, or specializing in areas like cybersecurity.
Bodyguards typically require specialized training and experience, such as military or law enforcement backgrounds. They often protect high-profile individuals and may advance to roles that involve coordinating security details or consulting.
Security officers usually have broader responsibilities, including implementing security protocols and managing compliance with regulations. Progressing in this career can lead to higher administrative roles or even security consultancy positions.
Understanding Security Protocols and Regulations
Security roles mandate strict adherence to industry standards and regulations. Security guards must know basic local safety laws and standards, such as the Private Security Guard Act.
Bodyguards need to understand advanced protocols, including risk assessment and crisis management strategies. Being well-versed in state and international laws is crucial.
Security officers must ensure that organizational security policies comply with legal requirements and best practices. Their roles often involve constant updates on new regulations and adapting protocols to maintain efficiency and safety.
Key Points:
- Basic and Advanced Training: Different roles require varying levels of specialized training and experience.
- Patrolling and Monitoring: Key tasks for entry-level guards, evolving into specialized or managerial roles.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Essential for all roles, with more complex responsibilities increasing further up the career ladder.
Tailoring Security Solutions to Your Unique Needs
Understanding the distinct roles of security guards, bodyguards, and security officers is essential for choosing the right security solution for your needs. Equally important is recognizing that modern security challenges demand advanced solutions, including proficient use of video surveillance systems, data analysis, and cybersecurity measures.
Selecting the optimal security solution requires a clear understanding of your specific requirements and the context in which security services will operate. For tailored advice and to ensure that your security system meets all your needs effectively, it is crucial to consult with experienced security providers.
Chisholm Security offers expertise in integrating cutting-edge surveillance technology with strategic planning to deliver comprehensive protection. Our team is equipped to assess your unique security needs and develop a customized solution that enhances safety and efficiency.
Ready to upgrade your security? Contact Chisholm Security today for a consultation, and let us help you design the perfect security system for your business or personal protection needs.

